920-726-4526
When it comes to efficiency, Rubber Pump Impellers play a vital role. These components help in transferring fluids in various industries. Selecting the right type can significantly enhance performance.
Rubber pump impellers are durable and versatile. They can handle different types of fluids, including corrosive ones. Their design can vary widely. Each variation has unique advantages and potential drawbacks.
While some choices lead to better efficiency, others may fall short. It's crucial to understand the specific applications of each type. An informed decision can prevent inefficiencies later. A reflective approach is needed when considering materials and designs. In the end, selecting the best rubber pump impeller is not just about performance; it's about ensuring longevity and reliability.
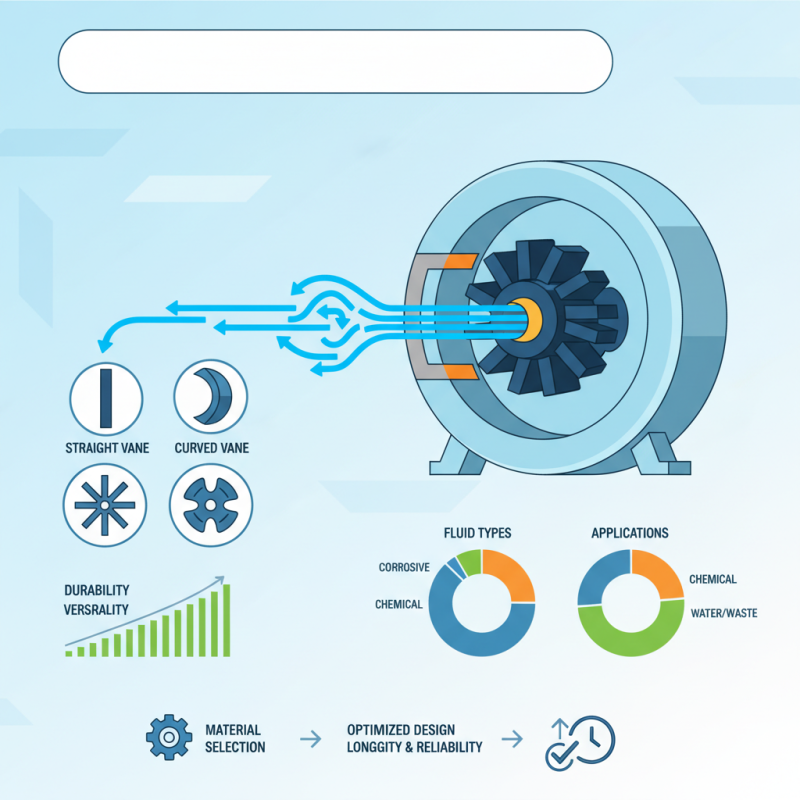
When considering rubber pump impellers, material selection is crucial. Various rubber types exhibit distinct properties that affect performance. Nitrile rubber, for instance, is widely preferred for its resistance to oil and fuel. However, it may not withstand extreme temperatures. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber excels in weather resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications. Yet, its compatibility with certain chemicals can be limiting.
Another commonly used material is natural rubber. It displays excellent elasticity and tensile strength. Reports indicate that natural rubber can extend the lifespan of pump components by reducing wear and tear. Nevertheless, its vulnerability to ozone degradation is a significant drawback. For aggressive chemical applications, neoprene rubber is a strong contender. It balances durability and flexibility but may fall short in extreme environments.
A 2021 industry analysis showed that about 35% of failures in pumping systems were linked to material selection errors. Often, users overlook the specific demands of their applications. Understanding these rubber types can significantly impact efficiency. Many operators report that improper impeller materials led to increased downtime. For optimal results, it’s essential to evaluate the operational environment closely.
When evaluating rubber pump impellers, several factors influence their efficiency. Material composition plays a crucial role. High-quality rubber provides better flexibility and durability. This leads to improved performance under varying operational conditions. However, not all rubber types are created equal. Some may wear down faster, impacting overall efficiency over time.
The design of the impeller is equally important. A well-designed impeller can enhance fluid flow and reduce turbulence. Optimal blade shape and angle contribute to maximizing performance. Yet, a design that works perfectly in one scenario may not be effective in another. It's essential to continuously assess the conditions where these impellers operate.
Finally, maintenance cannot be overlooked. Regular inspection ensures that wear and tear are addressed promptly. Even minor damage can lead to significant drops in efficiency. Outdated maintenance practices often result in overlooked inefficiencies. It's a common pitfall that many face, highlighting the need for constant vigilance in operations.
When choosing between centrifugal and positive displacement rubber impellers, several factors must be considered. Centrifugal impellers excel at moving large volumes of fluid quickly. They make use of rotational energy to propel fluids outward. This type of impeller is often seen in applications that require a steady flow rate. Their main advantage is efficiency in transporting low-viscosity liquids.
Positive displacement impellers, on the other hand, operate differently. They trap a fixed amount of fluid and then force it into the discharge line. This design is particularly beneficial for thicker fluids. These impellers can maintain constant flow regardless of pressure variations. However, if they are not used correctly, operational issues can arise. For instance, if pressure builds too high, the system may face mechanical failures.
Both designs have their shortcomings. Centrifugal impellers can struggle with viscous materials. Conversely, positive displacement designs might not handle rapid start-stop operations well. Understanding these nuances can be challenging but essential. Exploring real-world applications helps clarify their effectiveness in various scenarios. Each choice impacts efficiency, and careful consideration is necessary.
| Impeller Type | Efficiency (%) | Flow Rate (GPM) | Ideal Application | Maintenance Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Centrifugal | 75 | 50-500 | Water Transfer | Low |
| Positive Displacement | 85 | 10-300 | Viscous Fluids | Moderate |
| Flexible Impellers | 80 | 20-200 | Food & Beverage | Low |
| Gear Pumps | 78 | 5-100 | Oil Transfer | High |
Maintaining rubber pump impellers is crucial for optimal performance. According to a study by the Hydraulic Institute, proper maintenance can enhance efficiency by up to 30%. Regular inspections reveal wear patterns that can lead to reduced flow rates. It’s important to replace worn impellers promptly to prevent further damage.
Cleaning rubber impellers helps minimize buildup, which can impede performance. While certain chemicals may be effective, they could also degrade rubber over time. Using mild soaps and water is often recommended, but remember to rinse thoroughly. Lack of proper cleaning could lead to corrosion and inefficiency.
Monitoring operating conditions is another critical practice. Overheating can cause the rubber to lose elasticity, affecting its overall function. The ideal operating temperature varies; but keeping it within manufacturer guidelines can extend life. Simple checks can prevent costly repairs and downtime. Ignoring small issues may compromise the entire pump system. Regular maintenance is an investment, not just a task.
Innovations in rubber impeller designs have been pivotal in enhancing performance across various applications. One significant advancement is the development of composite materials that improve durability. These materials can withstand high temperatures and pressures, ensuring long-lasting efficiency. Additionally, the use of computer-aided design has allowed for more precise engineering. This leads to optimized flow dynamics, which enhances overall pump performance.
Another area of innovation focuses on the geometry of the impellers. Engineers are exploring non-conventional shapes to minimize turbulence. This change can result in smoother operation and lower energy consumption. Some designs incorporate ribbed structures to achieve better fluid dynamics, which can reduce noise levels during operation. While these advancements show promise, there's still much to explore in terms of materials and design.
However, not all innovations are flawless. Certain composite materials may not perform as expected. They could be susceptible to specific chemicals, which might limit their applications. Additionally, achieving the perfect balance between efficiency and durability remains a challenge. As research continues, the industry must remain open to testing and re-evaluating these new approaches to truly enhance rubber impeller performance.
This chart showcases various types of rubber pump impellers and their corresponding efficiency ratings. The data indicates that Axial Flow Impellers have the highest efficiency, while Progressive Cavity Impellers have the lowest. Innovations in rubber impeller designs play a significant role in enhancing these performance metrics.
5107 County Road C
Manitowoc, WI 54220
920-726-4526